Biography Chemists of Adolf von Baeyer
Johann Friedrich Wilhelm Adolf von Baeyer was born on October 31, 1835, in Berlin, Germany. Baeyer is a German chemist, recognized in 1905 for his work on organic dyes and compound substances hidroaromatik. Initially, he studied at Humboldt University in Berlin, Baeyer studied mathematics and physics. However, he soon discovered his love of the chemistry and moved to Heidelberg to study with Robert Bunsen in 1856. Bunsen was a famous chemist, who is widely known for perfecting the burner. Baeyer father a Prussian general. His mother was Jewish. Although ranking generals Baeyer father kapada science major interested. Baeyer apparently inherited his father. He MSUK Heidelberg University majoring in chemistry. In Heidelberg, studied in the laboratory Baeyer August Kekule, renowned organic chemist.
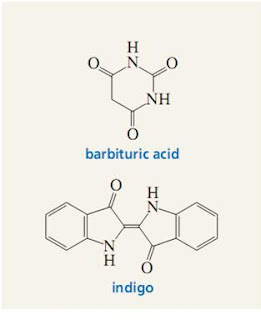
Professor named Bunsen and Kekulé. Bunsen emphasized the importance of experimentation and research, emphasizing the importance of the theory of Kekulé. Baeyer combine both. In 1858, Baeyer received his doctorate in chemistry from the University of Berlin. In 1871, he became a professor at Strasbourg and in 1875, Baeyer became Professor of Chemistry at the University of Munich. He was also awarded Davie Medal by the Royal Society of London in 1881, for his work with indigo. He received the Nobel Prize for chemistry (1905) for discovering artificial dyes, especially indigo synthesis (1880), and acid barbiturates (sleeping pills ingredients to make). He also discovered the chemical structure of indigo (1883).
Perhaps our readers have heard of "Indigo", plants from India. The word Indigo is a Spanish word meaning India. In Indonesia indogo called tom or Tarum. Of the plant is made of blue dye called indigo, which is used to dye batik fabrics. The Egyptians have been using indigo since 2000 BC. When the British captured India, brought to the UK indigo to dye cotton, wool, and clothing of the sailors. But indigo derived from plants are very expensive and the quality is not good.
When there is a war in Europe, the owners of the textile industry can not obtain indigo. So Baeyer seek immediate sense. He wanted to make a synthesis of indigo. Synthesis of man-made means. He began working in 1865. He worked hard for 15 years. In 1880 he managed to find indigo synthesis. Three years later (1883) he managed to find the chemical structure indogo, since that time the German chemist sitesis compete to make the other dyes, follow Baeyer. Prior to World War 1 (1914-1918), Germany became the largest manufacturer of dyestuffs in the world.
Professor named Bunsen and Kekulé. Bunsen emphasized the importance of experimentation and research, emphasizing the importance of the theory of Kekulé. Baeyer combine both. In 1858, Baeyer received his doctorate in chemistry from the University of Berlin. In 1871, he became a professor at Strasbourg and in 1875, Baeyer became Professor of Chemistry at the University of Munich. He was also awarded Davie Medal by the Royal Society of London in 1881, for his work with indigo. He received the Nobel Prize for chemistry (1905) for discovering artificial dyes, especially indigo synthesis (1880), and acid barbiturates (sleeping pills ingredients to make). He also discovered the chemical structure of indigo (1883).
Perhaps our readers have heard of "Indigo", plants from India. The word Indigo is a Spanish word meaning India. In Indonesia indogo called tom or Tarum. Of the plant is made of blue dye called indigo, which is used to dye batik fabrics. The Egyptians have been using indigo since 2000 BC. When the British captured India, brought to the UK indigo to dye cotton, wool, and clothing of the sailors. But indigo derived from plants are very expensive and the quality is not good.
When there is a war in Europe, the owners of the textile industry can not obtain indigo. So Baeyer seek immediate sense. He wanted to make a synthesis of indigo. Synthesis of man-made means. He began working in 1865. He worked hard for 15 years. In 1880 he managed to find indigo synthesis. Three years later (1883) he managed to find the chemical structure indogo, since that time the German chemist sitesis compete to make the other dyes, follow Baeyer. Prior to World War 1 (1914-1918), Germany became the largest manufacturer of dyestuffs in the world.
In addition to mixing the dye indigo, some Baeyer achievements include the discovery of dyes ptanein, observations polyacetylene, oxonium salts and uric acid derivatives. Bayer unite barbituik acid in 1864. This acid is used in surgery as a sedative or hypnotic. Baeyer also famous for his work in theoretical chemistry, developed the theory of 'saturation' (Spannung) the triple bond and saturated theory in small carbon rings. Baeyer Baeyer also the founder Chemical Co.. Adolf von Baeyer died on August 20, 1917 in Starnberg.

0 Response to "Biography Chemists of Adolf von Baeyer"
Post a Comment